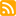1256
1256
 0
0
Giới thiệu HashSet
HashSet là lớp thuộc namespace System.Collections.Generic:
Biểu diễn một tập hợp các phần tử không trùng nhau.
Không truy cập phần tử thông qua index, tức là các phần tử trong set không có thứ tự (order). Do đó 2 set {1, 2, 3} và {3, 1, 2} là như nhau.
Vì các phần tử trong HashSet không có thứ tự nên khi: thứ tự các phần tử là quan trọng, là cần thiết cho xử lý của bạn thì không nên chọn loại data structure này.
HashSet là một cấu trúc nội bộ (internal structure) – nơi mà các phần tử được tìm kiếm và xác định một cách nhanh chóng.
Các cách khai báo và khởi tạo HashSet
Đối với kiểu dữ liệu nguyên thủy (Primitive Types) : int
Đối với kiểu dữ liệu tự định nghĩa : Rectangle
Kiểu dữ liệu tự định nghĩa Rectangle
Ghi chú:
Đối với kiểu dữ liệu nguyên thủy (Primitive Types) thì framework .NET đã cung cấp sẵn việc so sánh giữa các đối tượng với nhau rồi, nên chúng ta không cần phải cung cấp lại nữa.
Nhưng đối với những kiểu dữ liệu tự định nghĩa như: Rectangle, SinhVien, Animal,… thì khi cần so sánh đối tượng có bằng nhau hay không, chúng ta cần phải cung cấp thêm xử lý so sánh đối tượng bằng việc implement interface IEqualityComparer như trong bài viết này.
Các thuộc tính của HashSet
Các phương thức của HashSet
Thêm phần tử vào HashSet
Xóa phần tử khỏi HashSet
Kiểm tra HashSet có chứa một phần tử nào đó hay không
Các phương thức liên quan đến kiểm tra phần tử trong HashSet
Overlaps
・ Return True: nếu 2 set có phần tử giao nhau.
・ Return False: nếu 2 set không có chung phần tử nào.
HashSet – Overlaps
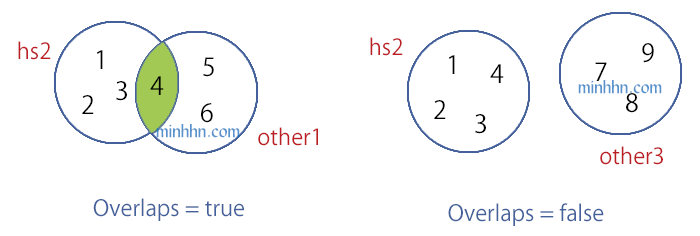
SetEquals
Return True: khi 2 set có các phần tử giống hệt nhau: cả Số Lượng + Giá Trị. Ngược lại return False
HashSet – SetEquals
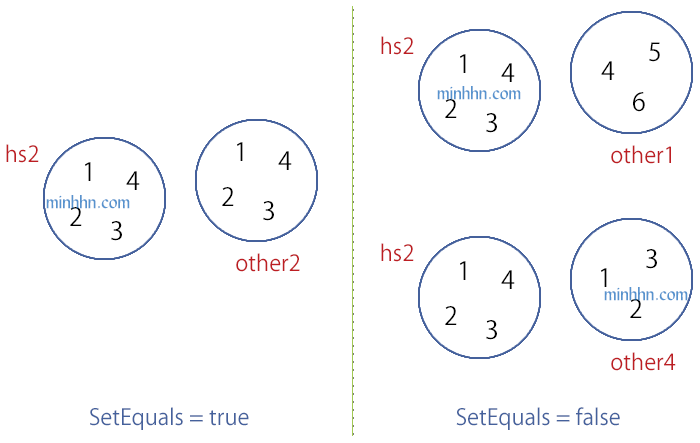
ExceptWith
Xóa phần tử của tập SET 1 nếu nó có trong tập SET 2
HashSet – ExceptWith
SymmetricExceptWith
Giữ lại các phần tử KHÔNG GIAO NHAU của 2 tập SET 1, SET 2 (Ngược với phương thức IntersectWith)
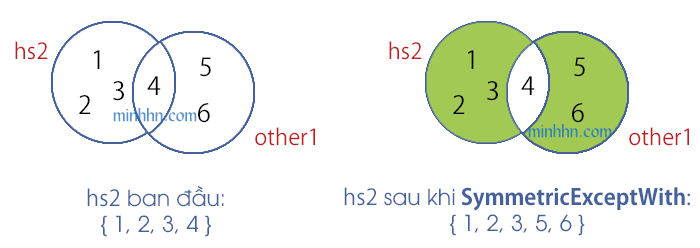
HashSet – SymmetricExceptWith
IntersectWith
Chỉ giữ lại các phần tử GIAO NHAU của 2 tập SET 1, SET 2 (Ngược với phương thức SymmetricExceptWith).
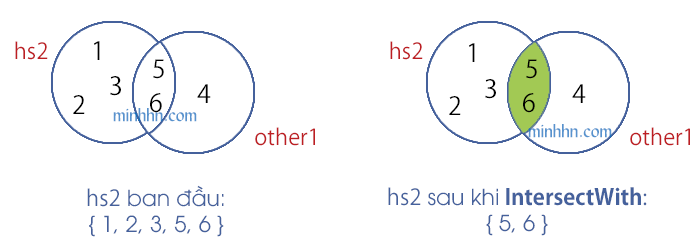
HashSet – IntersectWith
Các phương thức liên quan đến tập con trong HashSet
5.1. IsProperSubsetOf
Return True khi thỏa cả 2 điều kiện sau:
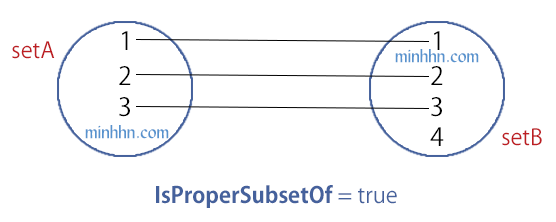
HashSet – IsProperSubsetOf
IsSubsetOf
Return True khi thỏa 1 trong 2 điều kiện sau:
Toàn bộ phần tử của tập bên trái ĐỀU THUỘC tập bên phải.
VÀ Số lượng phần tử của tập bên trái ÍT HƠN Số lượng phần tử của tập bên phải.
Toàn bộ phần tử của 2 tập bên trái và bên phải giống hệt nhau về: Số Lượng + Giá Trị (Giống với phương thức SetEquals)
Ngược lại thì return False.
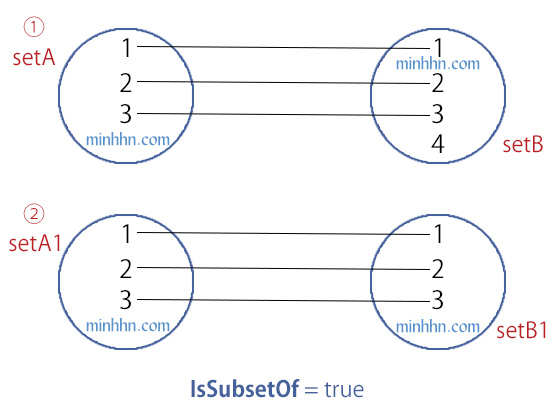
HashSet – IsSubsetOf
IsProperSupersetOf
Return True khi thỏa cả 2 điều kiện sau:
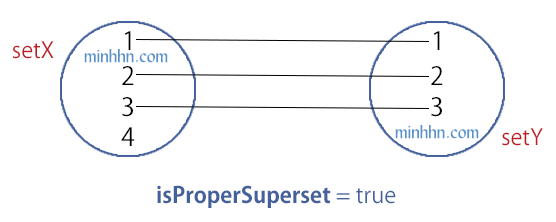
HashSet – IsProperSupersetOf
IsSupersetOf
Return True khi thỏa 1 trong 2 điều kiện sau:
Tập bên trái CHỨA toàn bộ phần tử của tập bên phải.
VÀ Số lượng phần tử của tập bên trái NHIỀU HƠN Số lượng phần tử của tập bên phải.
Toàn bộ phần tử của 2 tập bên trái và bên phải giống hệt nhau về: Số Lượng + Giá Trị
Giống với phương thức SetEquals.
Ngược lại thì return False.
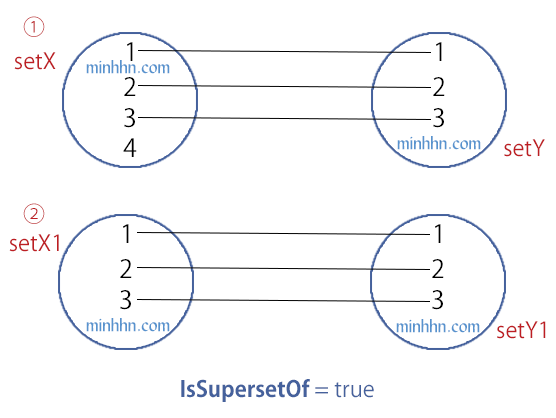
HashSet – IsSupersetOf
Full code example
HashSet là lớp thuộc namespace System.Collections.Generic:
Biểu diễn một tập hợp các phần tử không trùng nhau.
Không truy cập phần tử thông qua index, tức là các phần tử trong set không có thứ tự (order). Do đó 2 set {1, 2, 3} và {3, 1, 2} là như nhau.
Vì các phần tử trong HashSet không có thứ tự nên khi: thứ tự các phần tử là quan trọng, là cần thiết cho xử lý của bạn thì không nên chọn loại data structure này.
HashSet là một cấu trúc nội bộ (internal structure) – nơi mà các phần tử được tìm kiếm và xác định một cách nhanh chóng.
Các cách khai báo và khởi tạo HashSet
Đối với kiểu dữ liệu nguyên thủy (Primitive Types) : int
Mã:
// Khai báo
HashSet<int> hs1 = new HashSet<int>();
// Khai báo và khởi tạo 4 phần tử bằng tính năng Collection Initializer
HashSet<int> hs2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// Khai báo và khởi tạo 4 phần tử bằng cách cung cấp một [collection] IEnumerable, truyền vào 1 array
HashSet<int> hs3 = new HashSet<int>(collection: new[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 });Đối với kiểu dữ liệu tự định nghĩa : Rectangle
Mã:
// Khai báo
HashSet<Rectangle> hs4 = new HashSet<Rectangle>();
// Khai báo và khởi tạo bằng tính năng Collection Initializer + Object Initializer
HashSet<Rectangle> hs5 = new HashSet<Rectangle>() { new Rectangle { Width = 0, Height = 0 },
new Rectangle { Width = 1, Height = 1} };
// Khai báo HashSet với kiểu dữ liệu custom là: Rectangle,
// và [KHÔNG] chỉ định Equal Comparer để so sánh các phần tử, nên mặc định sẽ là: ObjectEqualityComparer.
HashSet<Rectangle> hsWithoutComparer = new HashSet<Rectangle>();
// comparer: new EqualComparer()
// Khai báo HashSet với kiểu dữ liệu custom là: Rectangle,
// và [CÓ] chỉ định custom(tự định nghĩa) Equality Comparer[RectEqualityComparer] để so sánh các phần tử.
HashSet<Rectangle> hsWithComparer = new HashSet<Rectangle>(
collection: new Rectangle[] { new Rectangle { Width = 0, Height = 0 },
new Rectangle { Width = 1, Height = 1} },
comparer: new RectEqualityComparer());
// comparer: new RectEqualityComparer()Kiểu dữ liệu tự định nghĩa Rectangle
Mã:
/// <summary>
/// Custom class: Rectangle
/// </summary>
internal class Rectangle
{
public int Width { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("Width = {0}, Height = {1}", Width, Height);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Custom Equality Comparer Object
/// </summary>
internal class RectEqualityComparer : IEqualityComparer<Rectangle>
{
public bool Equals(Rectangle x, Rectangle y)
{
// 2 hình chữ nhật bằng nhau khi Chiều dài và Chiều rộng bằng nhau
return x.Width == y.Width && x.Height == y.Height;
}
public int GetHashCode(Rectangle obj)
{
return $"{obj.Width} {obj.Height}".GetHashCode();
}
}Ghi chú:
Đối với kiểu dữ liệu nguyên thủy (Primitive Types) thì framework .NET đã cung cấp sẵn việc so sánh giữa các đối tượng với nhau rồi, nên chúng ta không cần phải cung cấp lại nữa.
Nhưng đối với những kiểu dữ liệu tự định nghĩa như: Rectangle, SinhVien, Animal,… thì khi cần so sánh đối tượng có bằng nhau hay không, chúng ta cần phải cung cấp thêm xử lý so sánh đối tượng bằng việc implement interface IEqualityComparer như trong bài viết này.
Các thuộc tính của HashSet
Mã:
// Lấy số lượng phần tử của 1 HashSet
int count = hs2.Count;
// count = 4
// Lấy thông tin comparer
IEqualityComparer<Rectangle> withoutComparer = hsWithoutComparer.Comparer;
// Output comparer mặc định:
// {System.Collections.Generic.ObjectEqualityComparer<MinhHoangBlog.Rectangle>}
IEqualityComparer<Rectangle> withComparer = hsWithComparer.Comparer;
// Output comparer tự định nghĩa:
// {MinhHoangBlog.RectEqualityComparer}Các phương thức của HashSet
Thêm phần tử vào HashSet
Mã:
// Thêm phần tử vào HashSet hs1
hs1.Add(1);
hs1.Add(2);
hs1.Add(3);
hs1.Add(4);
// Thêm phần tử có kiểu "primitive" và TRÙNG LẶP
// phần tử 4 sẽ không được thêm vào HashSet hs1, mà sẽ được bỏ qua.
hs1.Add(4);
// Thêm 1 phần tử có kiểu "custom" và TRÙNG LẶP
// ■ Trường hợp sử dụng comparer mặc định
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle { Width = 2, Height = 2 }; // Sử dụng từ khóa "new" tạo ra đối tượng mới r1
Rectangle r2 = r1; // Gán tham chiếu: r2 tham chiếu đến r1
Rectangle r3 = new Rectangle { Width = 2, Height = 2 }; // Sử dụng từ khóa "new" tạo ra đối tượng mới r3
hsWithoutComparer.Add(r1); // Add OK
hsWithoutComparer.Add(r2); // Bỏ quả không Add, vì ObjectEqualityComparer so sánh bộ nhớ tham chiếu,
// r1 và r2 cùng tham chiếu => không Add r2
// hsWithoutComparer:
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
// Tuy nhiên với r3 thì tuy giá trị giống nhau nhưng [bộ nhớ tham chiếu khác nhau] => Add OK
hsWithoutComparer.Add(r3);
// hsWithoutComparer:
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
// ■ Trường hợp sử dụng comparer tự định nghĩa
hsWithComparer.Add(r1); // Add OK
// hsWithComparer:
// {Width = 0, Height = 0}
// {Width = 1, Height = 1}
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
hsWithComparer.Add(r2); // Không Add r2 (vì r1 và r2 cùng tham chiếu)
hsWithComparer.Add(r3); // Không Add r3 (vì so sánh bằng RectEqualityComparer
// nên mặc dù khác tham chiếu, nhưng giá trị đã tồn tại rồi)Xóa phần tử khỏi HashSet
Mã:
// Xóa 1 phần tử cụ thể trong HashSet
hsWithComparer.Remove(r1);
// hsWithComparer:
// {Width = 0, Height = 0}
// {Width = 1, Height = 1}
// Xóa tất cả phần tử trong HashSet thỏa mãn điều kiện Width = 0
hsWithComparer.RemoveWhere(match: x => x.Width == 0);
// hsWithComparer:
// {Width = 1, Height = 1}
// Xóa tất cả phần tử trong HashSet
hsWithoutComparer.Clear();Kiểm tra HashSet có chứa một phần tử nào đó hay không
Mã:
// Kiểm tra chứa
bool isContain = hs1.Contains(3);
// trueCác phương thức liên quan đến kiểm tra phần tử trong HashSet
Overlaps
・ Return True: nếu 2 set có phần tử giao nhau.
・ Return False: nếu 2 set không có chung phần tử nào.

HashSet – Overlaps
Mã:
IEnumerable<int> other1 = new[] { 4, 5, 6 }; // Upcast vì Array : IEnumerable
IEnumerable<int> other2 = new[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
IEnumerable<int> other3 = new[] { 7, 8, 9 };
IEnumerable<int> other4 = new[] { 1, 2, 3 };
// Overlaps
bool isOverlap1 = hs2.Overlaps(other1);
// true, vì có chung phần tử: 4
bool isOverlap2 = hs2.Overlaps(other3);
// false, vì không có chung phần tử nàoSetEquals
Return True: khi 2 set có các phần tử giống hệt nhau: cả Số Lượng + Giá Trị. Ngược lại return False

HashSet – SetEquals
Mã:
// SetEquals
bool isEqual1 = hs2.SetEquals(other1);
bool isEqual2 = hs2.SetEquals(other4);
// false
bool isEqual3 = hs2.SetEquals(other2);
// trueExceptWith
Xóa phần tử của tập SET 1 nếu nó có trong tập SET 2

HashSet – ExceptWith
Mã:
HashSet<int> hs6 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// ExceptWith
hs6.ExceptWith(other1);
// hs6 { 1, 2, 3 } : đã xóa đi phần tử 4 vì có trong tập other1SymmetricExceptWith
Giữ lại các phần tử KHÔNG GIAO NHAU của 2 tập SET 1, SET 2 (Ngược với phương thức IntersectWith)

HashSet – SymmetricExceptWith
Mã:
// SymmetricExceptWith
hs2.SymmetricExceptWith(other1);
// hs2 { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 }
// Giữ lại các phần tử KHÔNG GIAO NHAU của 2 tập hs2 và other1 { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 }IntersectWith
Chỉ giữ lại các phần tử GIAO NHAU của 2 tập SET 1, SET 2 (Ngược với phương thức SymmetricExceptWith).

HashSet – IntersectWith
Mã:
// IntersectWith
hs2.SymmetricExceptWith(other1);
// hs2 { 5, 6 }
// Chỉ giữ lại các phần tử GIAO NHAU của 2 tập hs2 và other1 { 5, 6 }Các phương thức liên quan đến tập con trong HashSet
5.1. IsProperSubsetOf
Return True khi thỏa cả 2 điều kiện sau:
- Toàn bộ phần tử của tập bên trái ĐỀU THUỘC tập bên phải.
- Số lượng phần tử của tập bên trái ÍT HƠN Số lượng phần tử của tập bên phải.

HashSet – IsProperSubsetOf
Mã:
HashSet<int> setA = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setB = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// IsProperSubsetOf
bool isProperSubset = setA.IsProperSubsetOf(setB);
// true
HashSet<int> setA1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setB1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isProperSubset1 = setA1.IsProperSubsetOf(setB1);
// fase
HashSet<int> setA2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
HashSet<int> setB2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isProperSubset2 = setA2.IsProperSubsetOf(setB2);
// faseIsSubsetOf
Return True khi thỏa 1 trong 2 điều kiện sau:
Toàn bộ phần tử của tập bên trái ĐỀU THUỘC tập bên phải.
VÀ Số lượng phần tử của tập bên trái ÍT HƠN Số lượng phần tử của tập bên phải.
Toàn bộ phần tử của 2 tập bên trái và bên phải giống hệt nhau về: Số Lượng + Giá Trị (Giống với phương thức SetEquals)
Ngược lại thì return False.

HashSet – IsSubsetOf
Mã:
HashSet<int> setA = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setB = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// IsSubsetOf
bool isSubset = setA.IsSubsetOf(setB);
// true
HashSet<int> setA1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setB1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isSubset1 = setA1.IsSubsetOf(setB1);
// true
HashSet<int> setA2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
HashSet<int> setB2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isSubset2 = setA2.IsSubsetOf(setB2);
// faseIsProperSupersetOf
Return True khi thỏa cả 2 điều kiện sau:
- Tập bên trái CHỨA toàn bộ phần tử của tập bên phải.
- Số lượng phần tử của tập bên trái NHIỀU HƠN Số lượng phần tử của tập bên phải.

HashSet – IsProperSupersetOf
Mã:
HashSet<int> setX = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
HashSet<int> setY = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
// IsProperSupersetOf
bool isProperSuperset = setX.IsProperSupersetOf(setY);
// true
HashSet<int> setX1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setY1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isProperSuperset1 = setX1.IsProperSupersetOf(setY1);
// fase
HashSet<int> setX2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setY2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
bool isProperSuperset2 = setX2.IsProperSupersetOf(setY2);
// faseIsSupersetOf
Return True khi thỏa 1 trong 2 điều kiện sau:
Tập bên trái CHỨA toàn bộ phần tử của tập bên phải.
VÀ Số lượng phần tử của tập bên trái NHIỀU HƠN Số lượng phần tử của tập bên phải.
Toàn bộ phần tử của 2 tập bên trái và bên phải giống hệt nhau về: Số Lượng + Giá Trị
Giống với phương thức SetEquals.
Ngược lại thì return False.

HashSet – IsSupersetOf
Mã:
HashSet<int> setX = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
HashSet<int> setY = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
// IsSupersetOf
bool isSuperset = setX.IsSupersetOf(setY);
// true
HashSet<int> setX1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setY1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isSuperset1 = setX1.IsSupersetOf(setY1);
// true
HashSet<int> setX2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setY2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
bool isSuperset2 = setX2.IsSupersetOf(setY2);
// faseFull code example
Mã:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace MinhHoangBlog
{
internal class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*===============================*/
/* Khai báo */
/*===============================*/
// Khai báo
HashSet<int> hs1 = new HashSet<int>();
// Khai báo và khởi tạo 4 phần tử bằng tính năng Collection Initializer
HashSet<int> hs2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// Khai báo và khởi tạo 4 phần tử bằng cách cung cấp một [collection] IEnumerable, truyền vào 1 array
HashSet<int> hs3 = new HashSet<int>(collection: new[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 });
// Khai báo
HashSet<Rectangle> hs4 = new HashSet<Rectangle>();
// Khai báo và khởi tạo bằng tính năng Collection Initializer + Object Initializer
HashSet<Rectangle> hs5 = new HashSet<Rectangle>() { new Rectangle { Width = 0, Height = 0 },
new Rectangle { Width = 1, Height = 1} };
// Khai báo HashSet với kiểu dữ liệu custom là: Rectangle,
// và [KHÔNG] chỉ định comparer để so sánh các phần tử, nên mặc định sẽ là: [ObjectEqualityComparer]
HashSet<Rectangle> hsWithoutComparer = new HashSet<Rectangle>();
// comparer: new EqualComparer()
// Khai báo HashSet với kiểu dữ liệu custom là: Rectangle,
// và [CÓ] chỉ định comparer tự định nghĩa [RectEqualityComparer] để so sánh các phần tử.
HashSet<Rectangle> hsWithComparer = new HashSet<Rectangle>(
collection: new Rectangle[] { new Rectangle { Width = 0, Height = 0 },
new Rectangle { Width = 1, Height = 1} },
comparer: new RectEqualityComparer());
// comparer: new RectEqualityComparer()
/*===============================*/
/* Thuộc tính */
/*===============================*/
// Lấy số lượng phần tử của 1 HashSet
int count = hs2.Count;
// count = 4
// Lấy thông tin comparer
IEqualityComparer<Rectangle> withoutComparer = hsWithoutComparer.Comparer;
// Output comparer mặc định:
// {System.Collections.Generic.ObjectEqualityComparer<MinhHoangBlog.Rectangle>}
IEqualityComparer<Rectangle> withComparer = hsWithComparer.Comparer;
// Output comparer tự định nghĩa:
// {MinhHoangBlog.RectEqualityComparer}
/*===============================*/
/* Phương thức */
/*===============================*/
/*-------------------------------*/
/* Add elements */
/*-------------------------------*/
// Thêm phần tử vào HashSet hs1
hs1.Add(1);
hs1.Add(2);
hs1.Add(3);
hs1.Add(4);
// Thêm phần tử có kiểu "primitive" và TRÙNG LẶP
// phần tử 4 sẽ không được thêm vào HashSet hs1, mà sẽ được bỏ qua.
hs1.Add(4);
// Thêm 1 phần tử có kiểu "custom" và TRÙNG LẶP
// ■ Trường hợp sử dụng comparer mặc định
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle { Width = 2, Height = 2 }; // Sử dụng từ khóa "new" tạo ra đối tượng mới r1
Rectangle r2 = r1; // Gán tham chiếu: r2 tham chiếu đến r1
Rectangle r3 = new Rectangle { Width = 2, Height = 2 }; // Sử dụng từ khóa "new" tạo ra đối tượng mới r3
hsWithoutComparer.Add(r1); // Add OK
hsWithoutComparer.Add(r2); // Bỏ quả không Add, vì ObjectEqualityComparer so sánh bộ nhớ tham chiếu,
// r1 và r2 cùng tham chiếu => không Add r2
// hsWithoutComparer:
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
// Tuy nhiên với r3 thì tuy giá trị giống nhau nhưng [bộ nhớ tham chiếu khác nhau] => Add OK
hsWithoutComparer.Add(r3);
// hsWithoutComparer:
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
// ■ Trường hợp sử dụng comparer tự định nghĩa
hsWithComparer.Add(r1); // Add OK
// hsWithComparer:
// {Width = 0, Height = 0}
// {Width = 1, Height = 1}
// {Width = 2, Height = 2}
hsWithComparer.Add(r2); // Không Add r2 (vì r1 và r2 cùng tham chiếu)
hsWithComparer.Add(r3); // Không Add r3 (vì so sánh bằng RectEqualityComparer
// nên mặc dù khác tham chiếu, nhưng giá trị đã tồn tại rồi)
/*-------------------------------*/
/* Remove element */
/*-------------------------------*/
// Xóa 1 phần tử cụ thể trong HashSet
hsWithComparer.Remove(r1);
// hsWithComparer:
// {Width = 0, Height = 0}
// {Width = 1, Height = 1}
// Xóa tất cả phần tử trong HashSet thỏa mãn điều kiện Width = 0
hsWithComparer.RemoveWhere(match: x => x.Width == 0);
// hsWithComparer:
// {Width = 1, Height = 1}
// Xóa tất cả phần tử trong HashSet
hsWithoutComparer.Clear();
/*-------------------------------*/
/* Contains */
/*-------------------------------*/
// Kiểm tra chứa
bool isContain = hs1.Contains(3);
// true
/*-------------------------------*/
/* SET */
/*-------------------------------*/
IEnumerable<int> other1 = new[] { 4, 5, 6 }; // Upcast vì Array : IEnumerable
IEnumerable<int> other2 = new[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
IEnumerable<int> other3 = new[] { 7, 8, 9 };
IEnumerable<int> other4 = new[] { 1, 2, 3 };
// Overlaps
bool isOverlap1 = hs2.Overlaps(other1);
// true, vì có chung phần tử: 4
bool isOverlap2 = hs2.Overlaps(other3);
// false, vì không có chung phần tử nào
// SetEquals
bool isEqual1 = hs2.SetEquals(other1);
bool isEqual2 = hs2.SetEquals(other4);
// false
bool isEqual3 = hs2.SetEquals(other2);
// true
HashSet<int> hs6 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// ExceptWith
hs6.ExceptWith(other1);
// hs6 { 1, 2, 3 } : đã xóa đi phần tử 4 vì có trong tập other1
// SymmetricExceptWith
hs2.SymmetricExceptWith(other1);
// hs2 { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 }
// Giữ lại các phần tử KHÔNG GIAO NHAU của 2 tập hs2 và other1 { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 }
// IntersectWith
hs2.IntersectWith(other1);
// hs2 { 5, 6 }
// Chỉ giữ lại các phần tử GIAO NHAU { 5, 6 }
// ■ IsProperSubsetOf và IsSubsetOf
HashSet<int> setA = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setB = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// IsProperSubsetOf
bool isProperSubset = setA.IsProperSubsetOf(setB);
// true
// IsSubsetOf
bool isSubset = setA.IsSubsetOf(setB);
// true
HashSet<int> setA1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setB1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isProperSubset1 = setA1.IsProperSubsetOf(setB1);
// fase
bool isSubset1 = setA1.IsSubsetOf(setB1);
// true
HashSet<int> setA2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
HashSet<int> setB2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isProperSubset2 = setA2.IsProperSubsetOf(setB2);
// fase
bool isSubset2 = setA2.IsSubsetOf(setB2);
// fase
// ■ IsProperSupersetOf và IsSupersetOf
HashSet<int> setX = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
HashSet<int> setY = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
// IsProperSupersetOf
bool isProperSuperset = setX.IsProperSupersetOf(setY);
// true
// IsSupersetOf
bool isSuperset = setX.IsSupersetOf(setY);
// true
HashSet<int> setX1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setY1 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
bool isProperSuperset1 = setX1.IsProperSupersetOf(setY1);
// false
bool isSuperset1 = setX1.IsSupersetOf(setY1);
// true
HashSet<int> setX2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
HashSet<int> setY2 = new HashSet<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
bool isProperSuperset2 = setX2.IsProperSupersetOf(setY2);
// false
bool isSuperset2 = setX2.IsSupersetOf(setY2);
// false
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Custom class: Rectangle
/// </summary>
internal class Rectangle
{
public int Width { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("Width = {0}, Height = {1}", Width, Height);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Custom Equality Comparer Object
/// </summary>
internal class RectEqualityComparer : IEqualityComparer<Rectangle>
{
public bool Equals(Rectangle x, Rectangle y)
{
// 2 hình chữ nhật bằng nhau khi Chiều dài và Chiều rộng bằng nhau
return x.Width == y.Width && x.Height == y.Height;
}
public int GetHashCode(Rectangle obj)
{
return $"{obj.Width} {obj.Height}".GetHashCode();
}
}
}
Last edited by a moderator: